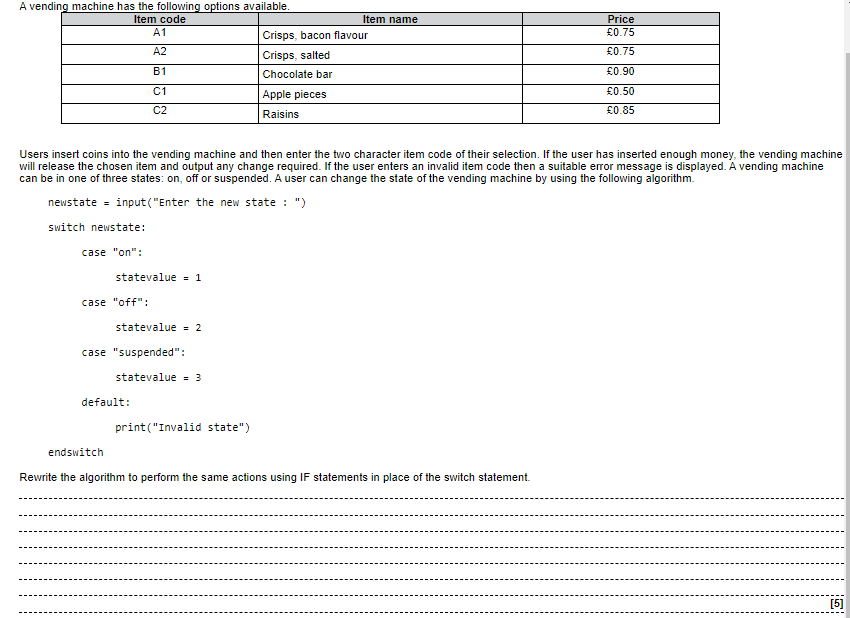
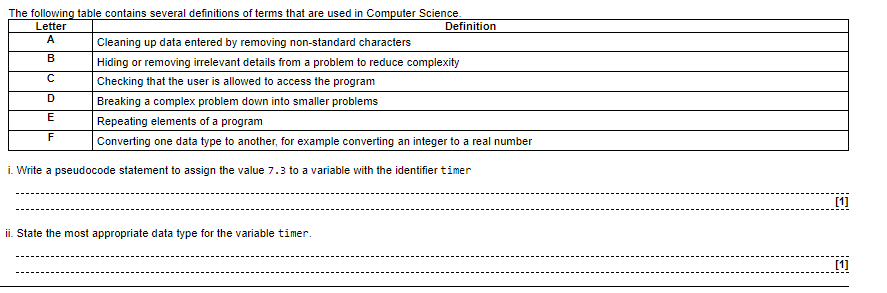
2.2.1 Programming fundamentals
The Use of Variables
Definition:
Variables are containers used to store data values in a program. Python has no command for declaring a variable, but a variable is created the moment you first assign a value to it.
Example:
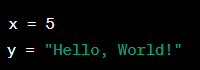
Significance:
Variables are essential to programming as they allow you to store and manipulate data values in your program. With variables, you can write more complex and dynamic code that can take user inputs, perform calculations, and output results.
The Use of Constants
Definition:
Constants are values that do not change during the execution of a program. In Python, constants are usually defined using uppercase letters.
Example:
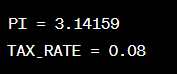
Significance:
Constants are useful in programs where you need to use a value repeatedly without changing it. For example, if you need to calculate the area of a circle, you can define the value of PI as a constant and use it in your calculations.
The Use of Operators
Definition:
Operators are symbols used to perform operations on variables and values in a program. Python has many types of operators, such as arithmetic operators, comparison operators, and logical operators.
Example:
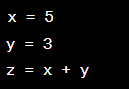
Significance:
Operators are important in programming as they allow you to perform mathematical operations, compare values, and control the flow of your program. With operators, you can write programs that can make decisions, loop through data, and manipulate values.
All operators in python
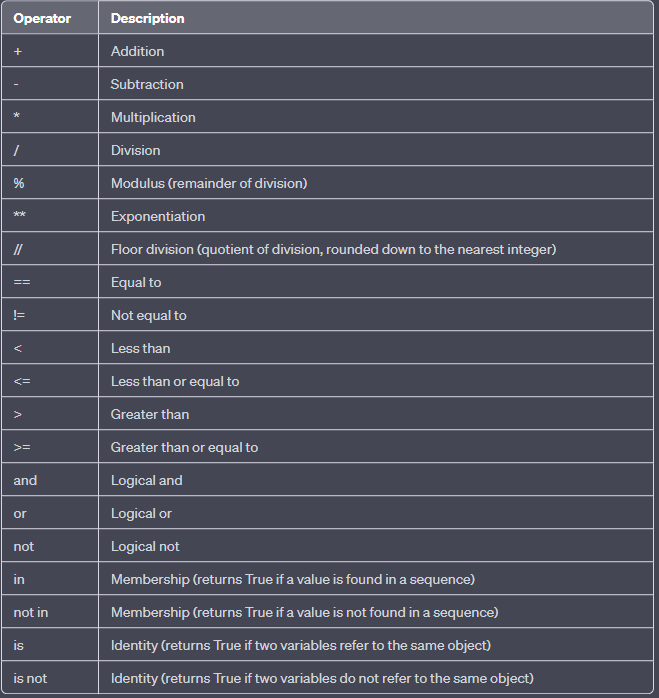
The Use of Inputs
Definition:
Inputs are data values that are provided to a program by a user or another part of the program. In Python, you can use the input() function to get input from the user.
Example:
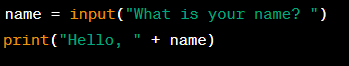
Significance:
Inputs are crucial in programming as they allow the program to interact with users and other parts of the program. With inputs, you can write programs that can take user inputs, make decisions based on those inputs, and output results based on those decisions.
The Use of Outputs
Definition:
Outputs are data values that a program produces as a result of its execution. In Python, you can use the print() function to output data values to the console.
Example:
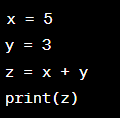
Significance:
Outputs are important in programming as they allow the program to communicate with users and other parts of the program. With outputs, you can write programs that can display results, error messages, or other information to the user.
The Use of Assignments
Definition:
Assignments are statements that assign values to variables in a program. In Python, you can use the = operator to assign values to variables.
Example:
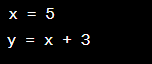
Significance:
Assignments are crucial in programming as they allow you to store and manipulate data values in your program. With assignments, you can write programs that can perform calculations, make decisions based on user inputs, and output results.
Programming constructs
The Use of Sequence in Programming
Definition:
Sequence is a programming construct that involves executing a series of statements one after another, in the order in which they appear in the code. This is the simplest type of programming construct and is used to perform a set of tasks in a specific order.
Example:
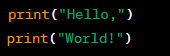
Significance:
Sequence is important in programming as it allows you to perform a set of tasks in a specific order. With sequence, you can write programs that can perform a series of operations, display messages to the user, or manipulate data values.
The Use of Selection in Programming
Definition:
Selection is a programming construct that involves making decisions based on certain conditions. This is done using conditional statements, such as if-else statements, which allow the program to take different paths depending on the value of certain variables or conditions.
Example:
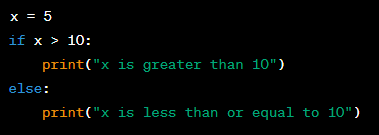
Significance:
Selection is important in programming as it allows you to write programs that can make decisions based on certain conditions. With selection, you can write programs that can take different paths based on user inputs, data values, or other factors.
The Use of Iteration in Programming
Definition:
Iteration is a programming construct that involves repeating a set of statements a certain number of times or until a certain condition is met. This is done using loops, such as for and while loops, which allow the program to repeat a set of statements until a certain condition is met.
Example:
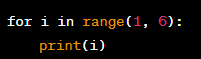
Significance:
Iteration is important in programming as it allows you to write programs that can perform repetitive tasks automatically. With iteration, you can write programs that can process large amounts of data, perform complex calculations, or interact with users in a specific way.
The Use of Count-Controlled Loops in Programming
Definition:
Count-controlled loops are a type of iteration that involves repeating a set of statements a certain number of times. This is done using a loop variable that counts the number of times the loop has been executed, and a loop condition that determines when the loop should terminate.
Example:
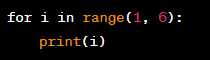
Significance:
Count-controlled loops are useful in programming as they allow you to repeat a set of statements a specific number of times. With count-controlled loops, you can write programs that can perform repetitive tasks, such as printing a set of numbers or processing a set of data.
The Use of Condition-Controlled Loops in Programming
Definition:
Condition-controlled loops are a type of iteration that involves repeating a set of statements until a certain condition is met. This is done using a loop condition that determines when the loop should terminate, based on the value of certain variables or conditions.
Example:
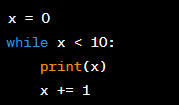
Significance:
Condition-controlled loops are useful in programming as they allow you to repeat a set of statements until a certain condition is met. With condition-controlled loops, you can write programs that can perform repetitive tasks, such as processing user inputs or manipulating data values, until a certain condition is met.
Past Paper Questions