2.1.3 Searching and sorting algorithms
Linear Search
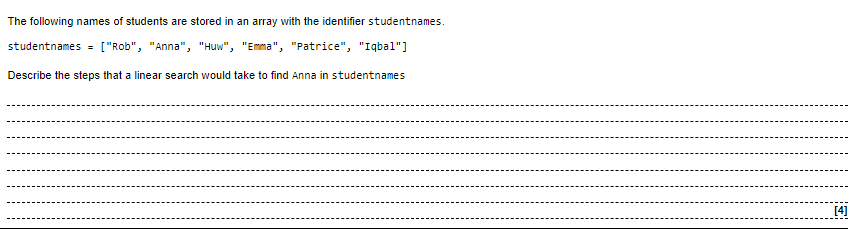
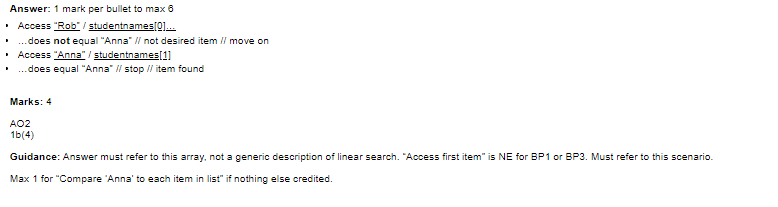
Understanding Linear Search Linear search is a simple searching algorithm that checks each element in a data set, one by one, until the desired element is found or until the end of the set is reached. This algorithm is sometimes called a brute-force search because it checks every element in the set, regardless of whether or not it matches the desired element.
Main Steps of Linear Search To perform linear search, you need to follow these steps:
- Start at the first element in the data set
- Check if the element matches the desired element
- If it does, stop searching and return the element's position
- If it doesn't, move on to the next element in the set and repeat the previous steps
- If the end of the data set is reached without finding the desired element, return a message indicating that it was not found
Applying Linear Search To apply linear search, you need a data set and a desired element to search for. Here are the steps to apply linear search:
- Start at the first element in the data set
- Check if the element matches the desired element
- If it does, stop searching and return the element's position
- If it doesn't, move on to the next element in the set and repeat the previous steps
- If the end of the data set is reached without finding the desired element, return a message indicating that it was not found
Identifying Linear Search Linear search can be identified in Python code or pseudocode by the use of a loop that checks each element in the data set until the desired element is found or the end of the set is reached.
Practice Questions and Answers
-
What is linear search? Answer: Linear search is a simple searching algorithm that checks each element in a data set, one by one, until the desired element is found or until the end of the set is reached.
-
What are the main steps of linear search? Answer: The main steps of linear search are starting at the first element in the data set, checking if the element matches the desired element, moving on to the next element in the set if it doesn't match, and returning the element's position if it does match.
-
How do you apply linear search to a data set? Answer: To apply linear search, you need to start at the first element in the data set, check if it matches the desired element, and move on to the next element if it doesn't match. Repeat this process until the desired element is found or the end of the set is reached.
-
How can you identify linear search in Python code or pseudocode? Answer: Linear search can be identified in Python code or pseudocode by the use of a loop that checks each element in the data set until the desired element is found or the end of the set is reached.
Useful link Bitesize watch the video at the bottom
Binary Search
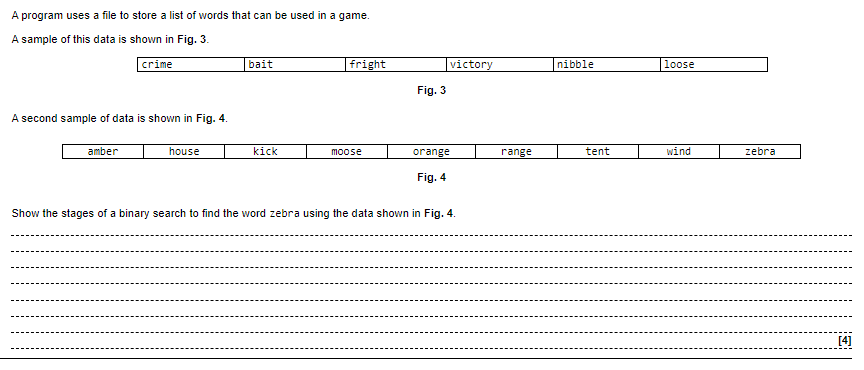
Binary search is a searching algorithm that is commonly used in computer science. It is an efficient algorithm that allows us to search for an item in a sorted list or array. This study guide will explain the main steps of binary search, its prerequisites, how to apply binary search to a data set, and how to identify it if given the python code or pseudocode.
- Understanding the main steps of binary search: Binary search involves dividing a sorted list or array into two equal halves repeatedly until the item being searched for is found or the search is exhausted. The main steps of binary search are as follows:
- Compare the middle item in the list with the target item.
- If the middle item is equal to the target item, the search is successful.
- If the middle item is greater than the target item, the search continues on the lower half of the list.
- If the middle item is less than the target item, the search continues on the upper half of the list.
- Repeat the above steps until the target item is found or the search is exhausted.
-
Prerequisites for binary search: To use binary search, the list or array must be sorted in ascending or descending order. This is important because binary search only works with sorted data.
-
Applying binary search to a data set: To apply binary search to a data set, the following steps should be taken:
- Sort the data set in ascending or descending order.
- Identify the middle item in the list.
- Compare the middle item with the target item.
- If the middle item is equal to the target item, the search is successful.
- If the middle item is greater than the target item, the search continues on the lower half of the list.
- If the middle item is less than the target item, the search continues on the upper half of the list.
- Repeat the above steps until the target item is found or the search is exhausted.
- Identifying binary search in code: Binary search can be identified in code by looking for the following characteristics:
- The data set is sorted.
- The search is divided into two equal halves repeatedly until the target item is found or the search is exhausted.
- The middle item is compared with the target item to determine the next search direction.
Practice questions:
- What is the main purpose of binary search?
- What are the prerequisites for using binary search?
- Describe the main steps of binary search.
- How do you apply binary search to a data set?
- How can you identify binary search in code?
Answers:
- The main purpose of binary search is to search for an item in a sorted list or array efficiently.
- The list or array must be sorted in ascending or descending order.
- The main steps of binary search are: compare the middle item in the list with the target item, continue the search on the lower or upper half of the list based on the comparison, and repeat until the target item is found or the search is exhausted.
- To apply binary search to a data set, you should sort the data set, identify the middle item, compare it with the target item, and repeat until the target item is found or the search is exhausted.
- Binary search can be identified in code by looking for sorted data, repeated division of the search into two equal halves, and comparison of the middle item with the target item.
Useful Link Bite Size Link Watch the video at the bottom
Bubble Sort
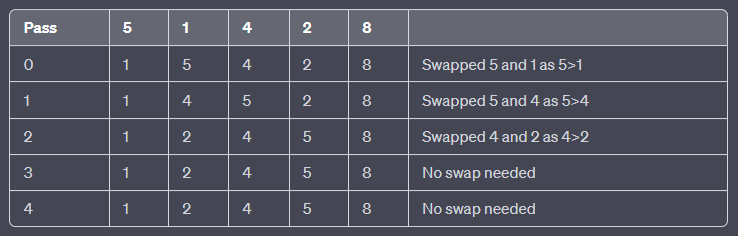
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order. The algorithm gets its name from the way the elements "bubble" to the top of the list during each iteration.
Main Steps of Bubble Sort The main steps of bubble sort are as follows:
- Compare the first and second elements in the list
- If they are in the wrong order, swap them
- Move to the next pair of adjacent elements and repeat the previous steps
- Continue this process until the end of the list is reached
- If any swaps were made during the previous iteration, repeat the entire process again
- Stop when a complete iteration is made without any swaps
Pre-Requisites for Bubble Sort Before applying bubble sort to a data set, you need to have a basic understanding of how to compare and swap elements in an array or list. It's also important to have a basic understanding of loops and conditional statements in programming.
Applying Bubble Sort To apply bubble sort to a data set, follow these steps:
- Start by comparing the first and second elements in the list
- If they are in the wrong order, swap them
- Move to the next pair of adjacent elements and repeat the previous steps
- Continue this process until the end of the list is reached
- If any swaps were made during the previous iteration, repeat the entire process again
- Stop when a complete iteration is made without any swaps
Example Bubble Sort
Identifying Bubble Sort Bubble sort can be identified in Python code or pseudocode by the use of a loop that repeatedly compares and swaps adjacent elements in the list until the list is sorted.
Practice Questions and Answers a. What is bubble sort? Answer: Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order.
b. What are the main steps of bubble sort? Answer: The main steps of bubble sort are comparing adjacent elements, swapping them if they are in the wrong order, and repeating this process until the list is sorted.
c. How do you apply bubble sort to a data set? Answer: To apply bubble sort to a data set, you need to repeatedly compare and swap adjacent elements in the list until it is sorted.
d. How can you identify bubble sort in Python code or pseudocode? Answer: Bubble sort can be identified in Python code or pseudocode by the use of a loop that repeatedly compares and swaps adjacent elements in the list until the list is sorted.
Usefull link on bitesize for bubble sort watch the video at the bottom
Merge Sort
Merge sort is a sorting algorithm that works by dividing an unsorted list into smaller, more manageable sub-lists, sorting those sub-lists, and then merging them back together to create a fully sorted list. It is a commonly used sorting algorithm because of its efficiency and ability to handle large sets of data.
Advantages of Merge Sort:
- Merge sort has a worst-case time complexity of O(n log n), which makes it very efficient for large data sets.
- It is a stable sorting algorithm, meaning that the relative order of equal elements is preserved.
- It can easily be implemented in parallel, which allows for even faster sorting of large data sets.
Disadvantages of Merge Sort:
- Merge sort requires additional memory space to store the sub-lists during the sorting process, which can make it less efficient for smaller data sets or in situations where memory is limited.
- While the worst-case time complexity is O(n log n), the constant factors involved can make it slower than other algorithms for smaller data sets.
Main Steps of Merge Sort: The main steps of merge sort are as follows:
- Divide the unsorted list into sub-lists, each containing one element (base case).
- Recursively merge adjacent sub-lists until there is only one sub-list remaining, which is the fully sorted list.
- Merge two sub-lists by comparing the first elements of each sub-list and placing them in order in a new, sorted list. Repeat this process until both sub-lists have been fully merged into the new list.
Applying Merge Sort: To apply merge sort, you first need an unsorted list of elements. You then divide that list into smaller sub-lists, sort those sub-lists, and then merge them back together into a fully sorted list.
Identifying Merge Sort: Merge sort can be identified in code or pseudocode by its recursive structure, which involves dividing the list into sub-lists and merging them back together.
Practice Questions and Answers:
-
What is merge sort? Answer: Merge sort is a sorting algorithm that divides an unsorted list into smaller sub-lists, sorts those sub-lists, and then merges them back together to create a fully sorted list.
-
What are the advantages of merge sort? Answer: Merge sort has a worst-case time complexity of O(n log n), it is a stable sorting algorithm, and it can easily be implemented in parallel.
-
What are the disadvantages of merge sort? Answer: Merge sort requires additional memory space, and the constant factors involved can make it slower than other algorithms for smaller data sets.
-
What are the main steps of merge sort? Answer: The main steps of merge sort are dividing the unsorted list into sub-lists, recursively merging adjacent sub-lists until there is only one sub-list remaining, and merging two sub-lists by comparing the first elements of each sub-list and placing them in order in a new, sorted list.
-
How do you apply merge sort to a data set? Answer: To apply merge sort, you need an unsorted list of elements. You then divide that list into smaller sub-lists, sort those sub-lists, and then merge them back together into a fully sorted list.
-
How can you identify merge sort in code or pseudocode? Answer: Merge sort can be identified in code or pseudocode by its recursive structure, which involves dividing the list into sub-lists and merging them back together.
Useful Bitesize link - Watch the video at teh bottom
Insertion Sort
Understanding Insertion Sort
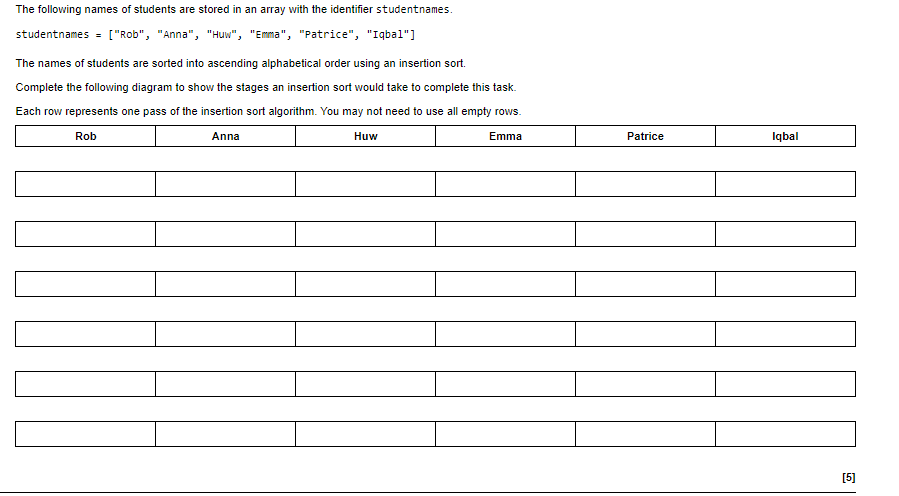
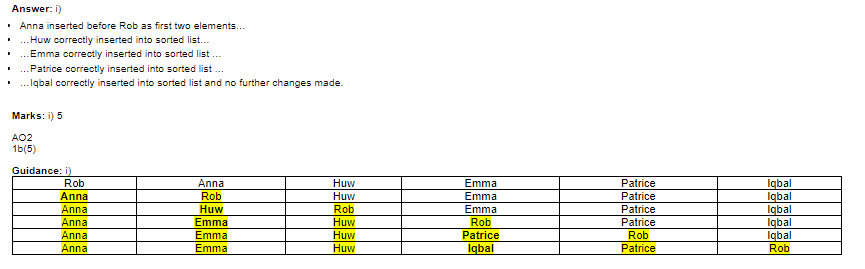
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that sorts a list of items by repeatedly inserting an unsorted item into its correct position within a sorted sublist.
Advantages of Insertion Sort
- It is easy to understand and implement.
- It performs well on small data sets and can be efficient on already partially sorted lists.
- It requires less memory than some other sorting algorithms.
Disadvantages of Insertion Sort
- It is less efficient than other sorting algorithms, especially on large data sets.
- It is not suitable for sorting large lists or data sets.
Applying Insertion Sort
To apply insertion sort to a list of items, the algorithm will iterate through the list, taking each unsorted item and inserting it into the correct position within a sorted sublist. Here are the steps to apply insertion sort:
1. Start at the second item in the list, as the first item is already considered sorted.
2. Compare the second item with the first item. If the second item is smaller, swap them.
3. Move on to the third item and compare it to the first and second items. Insert it into the correct position in the sorted sublist.
4. Continue this process for each remaining item in the list, inserting it into the correct position within the sorted sublist.
5. The list is now sorted.
Identifying Insertion Sort
Insertion sort can be identified in Python code or pseudocode by the use of a loop that iterates through each item in the list and inserts it into the correct position within a sorted sublist.
Practice Questions and Answers
a. What is insertion sort?
Answer: Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that sorts a list of items by repeatedly inserting an unsorted item into its correct position within a sorted sublist.
b. What are the advantages of insertion sort?
Answer: The advantages of insertion sort are that it is easy to understand and implement, performs well on small data sets, and requires less memory than some other sorting algorithms.
c. What are the disadvantages of insertion sort?
Answer: The disadvantages of insertion sort are that it is less efficient than other sorting algorithms, especially on large data sets, and it is not suitable for sorting large lists or data sets.
d. How do you apply insertion sort to a list of items?
Answer: To apply insertion sort to a list of items, the algorithm will iterate through the list, taking each unsorted item and inserting it into the correct position within a sorted sublist.
e. How can you identify insertion sort in Python code or pseudocode?
Answer: Insertion sort can be identified in Python code or pseudocode by the use of a loop that iterates through each item in the list and inserts it into the correct position within a sorted sublist.