1.6.2 Legislation relevant to Computer Science
Introduction:
In this study guide, we will discuss the legislation relevant to computer science. This includes the Data Protection Act 2018, Computer Misuse Act 1990, Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988, and software licenses such as open source and proprietary. We will cover the purpose of each piece of legislation and the specific actions it allows or prohibits. We will also discuss the need to license software and the features of open source and proprietary software. Lastly, we will recommend a type of license for a given scenario including the benefits and drawbacks.
The Data Protection Act 2018:
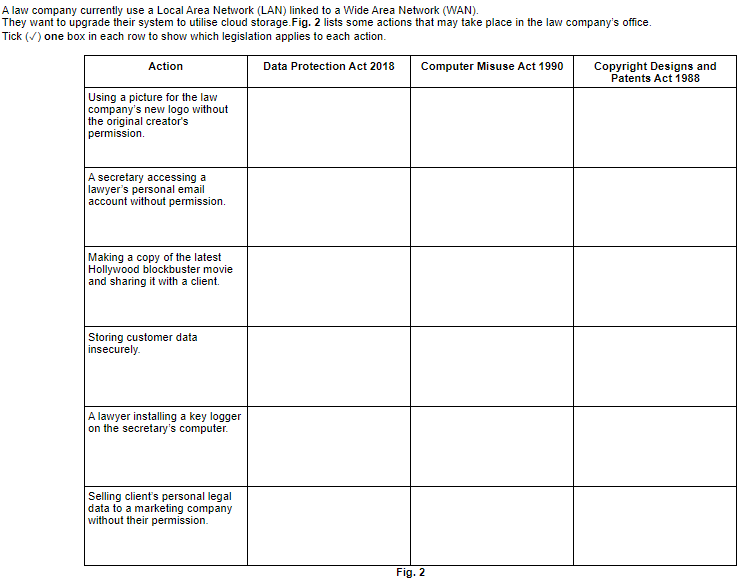
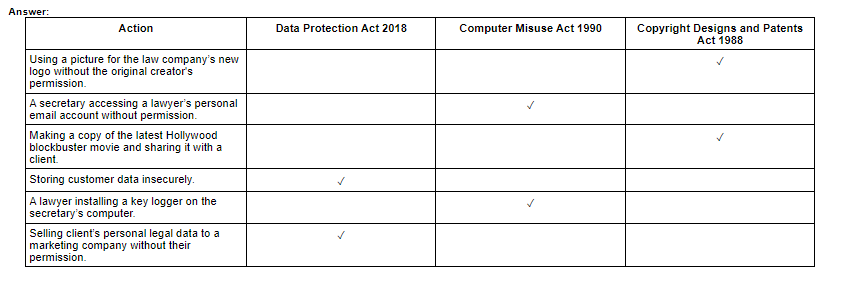
The Data Protection Act 2018 is a UK law that regulates the processing of personal data. It sets out rules for how personal data should be collected, processed, stored, and shared. The purpose of this legislation is to protect individuals' privacy and ensure that their personal data is used appropriately. It prohibits the processing of personal data without the individual's consent, except in specific circumstances. It also gives individuals the right to access their personal data and request that it be corrected or deleted.
Computer Misuse Act 1990:
The Computer Misuse Act 1990 is a UK law that makes it illegal to access computer systems without authorization. The purpose of this legislation is to prevent unauthorized access to computer systems and to protect computer systems from unauthorized access, modification, or destruction. It prohibits activities such as hacking, spreading viruses or malware, and using someone else's username and password to access a computer system. It also makes it illegal to create or distribute tools or programs that can be used for hacking.
Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988:
The Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988 is a UK law that protects the rights of creators of original works, such as software programs, music, and books. The purpose of this legislation is to prevent others from copying or using someone else's work without permission. It allows creators to control how their work is used, and they can choose to license it for use by others. It prohibits activities such as copying, distributing, or adapting someone else's work without permission.
Software Licenses:
Software licenses are legal agreements between the software developer and the user that define the terms of use for the software. There are two main types of software licenses: open source and proprietary.
Open Source:
Open source software is software that is freely available to use, modify, and distribute. The source code is also available, meaning that users can see and modify the code. The purpose of open source software is to encourage collaboration and innovation, as well as to ensure that software remains accessible to everyone. However, open source software does not provide any guarantees or warranties, and the user assumes all risks associated with using it.
Proprietary:
Proprietary software is software that is owned by a company or individual and is licensed for use. The source code is not available, meaning that users cannot modify or redistribute the software. The purpose of proprietary software is to protect the intellectual property of the developer and provide a revenue stream. However, proprietary software can be expensive, and users may not have the same level of control over the software as they would with open source software.
Recommendations for Software Licenses:
The type of license recommended for a given scenario will depend on the specific needs and circumstances of the user. For example, if the user is looking for a low-cost solution and wants to modify the software, open source software may be the best choice. If the user needs a reliable and supported solution, proprietary software may be the best choice. It is important to carefully evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of each type of license before making a decision.
Questions:
- What is the purpose of the Data Protection Act 2018?
- What actions does the Data Protection Act 2018 allow or prohibit?
- What is the purpose of the Computer Misuse Act 1990?
- What actions does the Computer Misuse Act 1990 allow or prohibit?
- What is the purpose of the Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988?
- What actions does the Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988 allow or prohibit?
- What is a software license and why is it needed?
- What is the difference between open source and proprietary software?
- What are the features of open source software?
- What are the features of proprietary software?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of open source software?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of proprietary software?
- When would you recommend using open source software?
- When would you recommend using proprietary software?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of using a proprietary software license?
Answers:
- The purpose of the Data Protection Act 2018 is to protect the privacy and personal data of individuals.
- The Data Protection Act 2018 allows individuals to have control over their personal data and gives them the right to access, correct, and delete their personal data. It prohibits the unauthorized use, disclosure, or sale of personal data.
- The purpose of the Computer Misuse Act 1990 is to prevent unauthorized access to computer systems.
- The Computer Misuse Act 1990 prohibits unauthorized access to computer systems, including hacking and the creation or distribution of malware.
- The purpose of the Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988 is to protect the rights of creators of original works.
- The Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988 allows creators of original works to control the use, distribution, and reproduction of their works. It prohibits the unauthorized copying or distribution of copyrighted material.
- A software license is a legal agreement between the software developer and the user that defines the terms and conditions for using the software.
- Open source software is software that is made freely available to the public and allows users to view and modify the source code. Proprietary software is software that is owned by a company and is not available for the public to view or modify.
- The features of open source software include free access to the software, the ability to view and modify the source code, and a community of developers who contribute to the software's development.
- The features of proprietary software include restricted access to the software, limited or no access to the source code, and dedicated technical support from the software vendor.
- The benefits of open source software include free access to the software, the ability to customize the software to fit specific needs, and the availability of a large community of developers who contribute to the software's development. The drawbacks of open source software include a lack of dedicated technical support and potential security risks.
- The benefits of proprietary software include dedicated technical support from the vendor, a wider range of features and functionalities, and greater security measures. The drawbacks of proprietary software include the cost of purchasing and maintaining the software, a lack of transparency in how the software operates, and limited customization options.
- Open source software may be recommended in scenarios where cost is a concern and customization options are important.
- Proprietary software may be recommended in scenarios where dedicated technical support and greater security measures are required.
- The benefits of using a proprietary software license include greater control over the use and distribution of the software, dedicated technical support from the vendor, and the ability to generate revenue from the sale of the software.
Past Papers Questions