Study Guide for Operating System and User Interface
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is the most important type of system software that manages computer hardware and software resources. It provides a platform for software programs to run on a computer. The OS controls and manages all hardware devices such as the processor, memory, input/output (I/O) devices and network devices.
Functions of an Operating System
- Process Management: The OS manages the creation, scheduling, and execution of processes on a computer system.
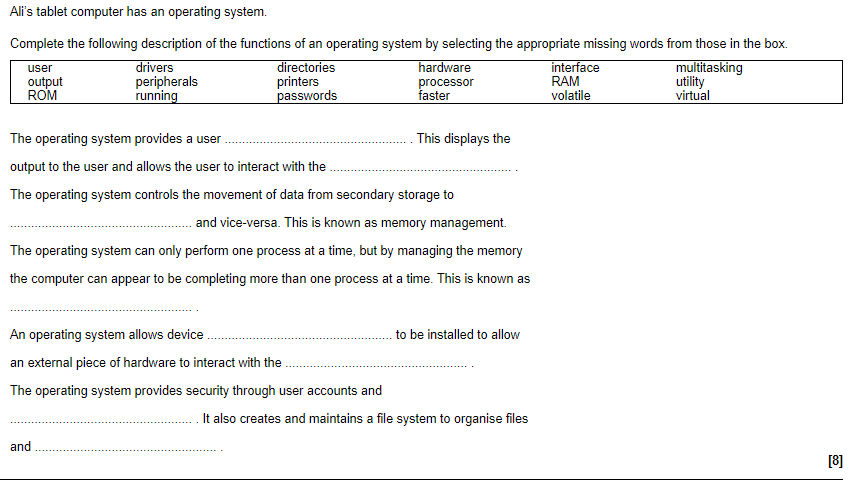
- Memory Management: The OS allocates and deallocates memory for processes and manages the transfer of data between memory.
- Device Management: The OS manages all input/output (I/O) devices connected to a computer, including printers, keyboards, and mice.
- File Management: The OS manages the creation, deletion, and organization of files and directories on a computer.
- User Interface: A user interface (UI) is the way in which a user interacts with a computer system
User Interface
A user interface (UI) is the way in which a user interacts with a computer system. It provides a graphical representation of a computer system's capabilities and makes it easy for users to use software applications. A UI can be graphical, command-line or a combination of both.
Features of a User Interface
- Ease of Use: A good UI should be easy to use and should provide a clear and understandable way to access the computer system's features.
- Consistency: A UI should be consistent in its layout and design across all software applications.
- Customizability: A UI should allow users to customize it according to their preferences.
- Visual Appeal: A UI should be visually appealing, with attractive graphics and fonts.
- Accessibility: A UI should be accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.
Types of User Interfaces
There are three main types of user interfaces:
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
A Graphical User Interface (GUI) uses graphical elements such as icons, buttons, and menus to allow users to interact with a computer system. It is the most common type of UI used in modern operating systems.
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
A Command-Line Interface (CLI) allows users to interact with a computer system by typing commands on a keyboard. It is a powerful interface used by developers and system administrators to perform complex tasks quickly and efficiently.
Natural Language Interface
A Natural Language Interface (NLI) allows users to interact with a computer system using natural language. Users can type or speak commands in plain English, and the computer system can interpret and execute them.
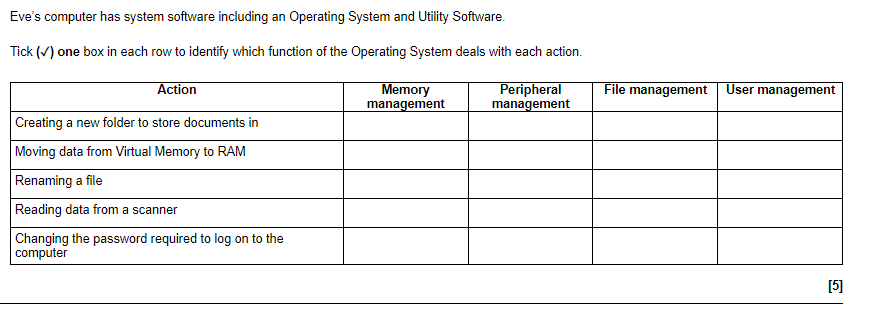
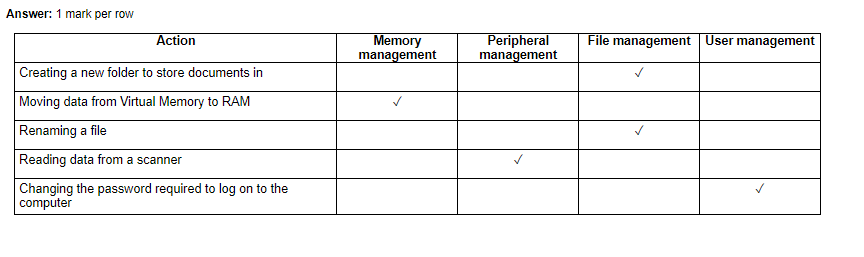
Memory Management
What is memory management?
Memory management is the process by which an operating system manages computer memory. It involves allocating and deallocating memory for different applications and processes, and ensuring that each process has access to the memory it needs.
How does memory management work?
Memory management works by dividing computer memory into different regions, each with its own specific purpose. When an application or process requires memory, the operating system allocates a portion of memory from the appropriate region. When the application or process no longer needs the memory, the operating system deallocates the memory and returns it to the appropriate region.
What is multitasking, and how does memory management enable it?
Multitasking is the ability of an operating system to run multiple applications or processes at the same time. Memory management enables multitasking by allocating memory to different applications or processes as needed, and ensuring that each process has access to the memory it needs. This allows multiple applications or processes to run simultaneously withou
Managing Data Transfer in an Operating System
An operating system is responsible for managing the transfer of data between devices and the processor. This process needs to be managed effectively to ensure that data is transferred efficiently and without errors.
What is Data Transfer?
Data transfer is the process of moving data between devices and the processor. This can include transferring data from a hard drive to the processor, from a USB drive to the processor, or from a network connection to the processor.
Why is Data Transfer Management Important?
Effective data transfer management is important for several reasons. First, it ensures that data is transferred efficiently and without errors, which can improve the performance of the system. Second, it can help prevent data loss or corruption, which can be costly and time-consuming to fix. Finally, it can help ensure that the system is secure by preventing unauthorized access to data.
How is Data Transfer Managed?
Data transfer is managed by the operating system, which uses a variety of techniques to ensure that data is transferred efficiently and without errors. These techniques include:
-
Buffering: Buffering involves temporarily storing data in a buffer before it is transferred to the processor. This can help prevent data loss or corruption and can improve the performance of the system.
-
Caching: Caching involves storing frequently accessed data in a cache, which can improve the performance of the system by reducing the time it takes to access the data.
-
Interrupts: Interrupts are signals sent to the processor by devices to request its attention. This can help ensure that data is transferred in a timely and efficient manner.
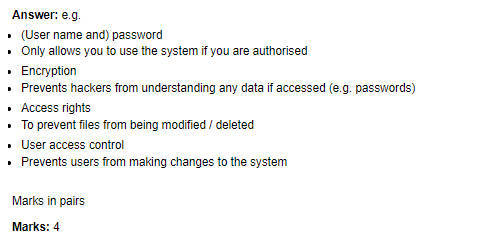
User Management Functions of an Operating System
An operating system provides several user management functions to manage user accounts, access rights, and security. Understanding these functions is essential for ensuring the security and proper use of a system.
Allocation of an Account
An operating system allows administrators to create user accounts and assign privileges to users based on their roles and responsibilities. User accounts can be created for individuals or groups, and each account is assigned a username and password for authentication purposes.
Access Rights
Access rights refer to the level of access that a user has to files, directories, and other resources on a system. Access rights can be assigned based on the principle of least privilege, which means that users are only given access to the resources that they need to perform their job.
Security
Operating systems provide various security measures to protect user accounts and system resources. These measures include encryption, password policies, and two-factor authentication. It is essential to follow these security measures to prevent unauthorized access to the system.
By understanding the user management functions of an operating system, users can ensure the proper use of a system while also maintaining its security.
Questions
-
What is an operating system? An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, providing a platform for software programs to run on a computer.
-
What are the functions of an operating system? The functions of an operating system include process management, memory management, device management, file management, and user interface.
-
What is memory management? Memory management is the process by which an operating system manages computer memory, including allocating and deallocating memory for different applications and processes and ensuring that each process has access to the memory it needs.
-
What are the types of user interfaces? The three main types of user interfaces are graphical user interface (GUI), command-line interface (CLI), and natural language interface (NLI).
-
What is data transfer management? Data transfer management is the process of managing the transfer of data between devices and the processor in an operating system, ensuring that data is transferred efficiently and without errors.
-
What are the user management functions of an operating system? The user management functions of an operating system include the allocation of user accounts, access rights, and security measures such as encryption, password policies, and two-factor authentication.
-
Why is understanding user management functions important for system security? Understanding user management functions is important for system security because it helps ensure the proper use of the system while also maintaining its security, preventing unauthorized access to the system.
Answers
-
What is an operating system? An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, providing a platform for software programs to run on a computer.
-
What are the functions of an operating system? The functions of an operating system include process management, memory management, device management, file management, and user interface.
-
What is memory management? Memory management is the process by which an operating system manages computer memory, including allocating and deallocating memory for different applications and processes and ensuring that each process has access to the memory it needs.
-
What are the types of user interfaces? The three main types of user interfaces are graphical user interface (GUI), command-line interface (CLI), and natural language interface (NLI).
-
What is data transfer management? Data transfer management is the process of managing the transfer of data between devices and the processor in an operating system, ensuring that data is transferred efficiently and without errors.
-
What are the user management functions of an operating system? The user management functions of an operating system include the allocation of user accounts, access rights, and security measures such as encryption, password policies, and two-factor authentication.
-
Why is understanding user management functions important for system security? Understanding user management functions is important for system security because it helps ensure the proper use of the system while also maintaining its security, preventing unauthorized access to the system.