1.4.1 Threats to computer systems and networks
Computers and networks are essential parts of our daily lives. They help us in many ways, from sending emails to shopping online. However, they are also vulnerable to attacks. In this study guide, we will discuss the different types of threats that can affect computer systems and networks, and how they are used.
Malware:
Malware is a type of software that is designed to damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system or network. Malware can be introduced to a system through various means such as phishing emails, infected websites, and infected USB drives. Examples of malware include viruses, worms, trojan horses, and ransomware.
Social engineering:
Social engineering is a technique used by attackers to manipulate people into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that can lead to a security breach. Examples of social engineering attacks include phishing and spear-phishing, where attackers use emails or messages that appear legitimate to trick users into providing sensitive information.
Brute-force attacks:
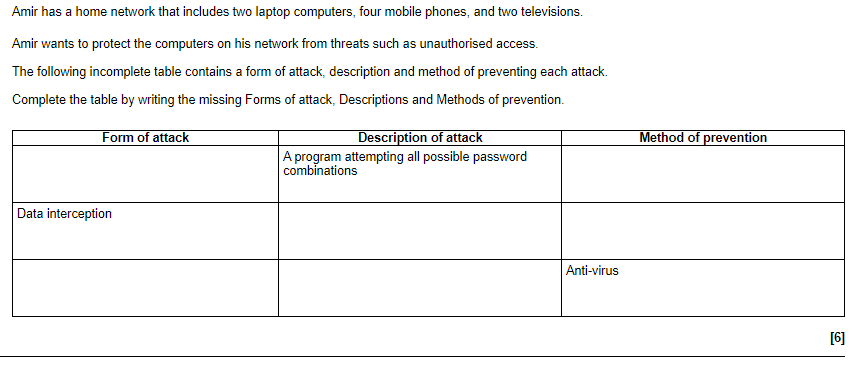
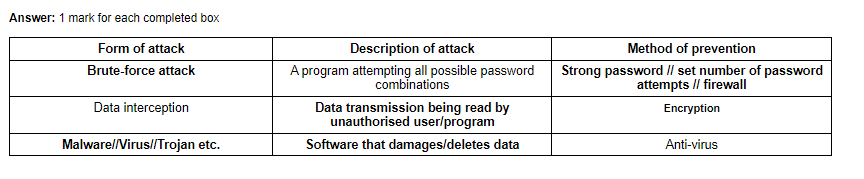
Brute-force attacks are a method of cracking passwords by trying all possible combinations of characters until the correct one is found. These attacks can be time-consuming, but with modern computing power, they can be carried out relatively quickly.
Denial of service (DoS) attacks: DoS attacks are a type of attack that aims to disrupt the normal functioning of a network or website by overwhelming it with traffic. This can cause the network or website to become slow or unavailable, leading to loss of service for legitimate users.
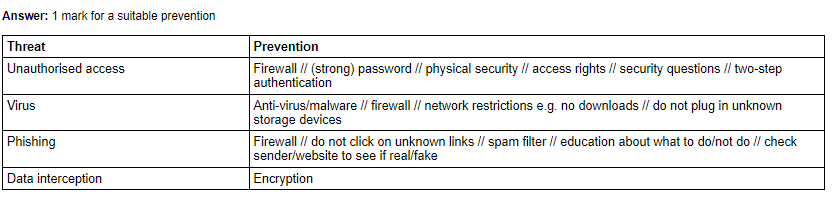
Data interception and theft: Data interception and theft involve attackers intercepting and stealing sensitive data from a network or computer system. This can be done through various means, such as exploiting vulnerabilities in the system, using malware to capture data, or using social engineering techniques to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
SQL injection: SQL injection is a type of attack that targets databases by injecting malicious SQL code into input fields on a website. This can allow attackers to access or modify data stored in the database.
Conclusion: Threats to computer systems and networks are ever-present, and it is important to be aware of them to protect ourselves and our information. By understanding the different types of attacks and how they are carried out, we can take steps to mitigate their impact. It is also important to use best practices such as using strong passwords, keeping software up-to-date, and being vigilant against social engineering attacks.
Denial of Service Attacks
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks are malicious attempts to disrupt the availability of a computer system or network. These attacks aim to overwhelm the target with a flood of illegitimate requests, causing it to become inaccessible to legitimate users. In this study guide, we will explore the different types of DoS attacks, their impact, and the strategies to mitigate and prevent such attacks.
1. Understanding Denial of Service Attacks:
- Definition: A Denial of Service attack is a deliberate attempt to make a computer system or network unavailable to its intended users.
- Objective: Attackers seek to overwhelm the target's resources, such as bandwidth, processing power, or memory, rendering the system or network unresponsive.
- Significance: DoS attacks can disrupt essential services, cause financial losses, damage reputation, and impede regular operations.
2. Types of Denial of Service Attacks:
- Network-Based Attacks: These attacks flood the network infrastructure with a massive volume of traffic, consuming bandwidth and overwhelming routers, switches, and servers.
- Application Layer Attacks: These attacks target vulnerabilities in specific applications or services, overwhelming them with requests or exploiting their weaknesses.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks: DDoS attacks involve multiple compromised devices, forming a botnet, which simultaneously flood the target with traffic.
3. Impact of Denial of Service Attacks:
- Service Disruption: Attackers aim to render the target system or network inaccessible to legitimate users, causing inconvenience and frustration.
- Financial Losses: Downtime and disruption can result in significant financial losses for businesses, including lost sales, productivity, and recovery costs.
- Reputational Damage: Organizations affected by DoS attacks may suffer reputational harm as customers lose trust and confidence in their ability to provide reliable services.
- Legal Consequences: Perpetrators of DoS attacks can face legal repercussions, as such activities are illegal and punishable under cybercrime laws.
4. Mitigation and Prevention:
- Network Monitoring: Implementing robust network monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems can help identify and mitigate DoS attacks in real-time.
- Bandwidth Management: Employing bandwidth management techniques can help mitigate the impact of DoS attacks by prioritizing legitimate traffic and reducing the impact of malicious traffic.
- Intrusion Prevention Systems: Deploying intrusion prevention systems can detect and block DoS attack traffic, preventing it from reaching the target.
- Redundancy and Load Balancing: Setting up redundant systems and load balancers can distribute traffic and prevent a single point of failure during an attack.
- Incident Response Plans: Developing and regularly testing incident response plans can ensure a swift and effective response to mitigate the impact of DoS attacks.
Data Interception and Theft
Data interception and theft refer to unauthorized access, monitoring, or acquisition of sensitive information by malicious individuals or entities. In this study guide, we will explore the concept of data interception and theft, its significance, and the measures to protect data from such security breaches.
1. Understanding Data Interception and Theft:
- Definition: Data interception and theft involve unauthorized access, monitoring, or acquisition of sensitive data, including personal, financial, or confidential information.
- Methods of Interception: Attackers may employ techniques like network eavesdropping, phishing, malware, or exploiting vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to data.
- Significance: Data interception and theft pose significant risks, including identity theft, financial loss, privacy breaches, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
2. Common Techniques Used:
- Network Eavesdropping: Attackers intercept data transmitted over networks, such as Wi-Fi or unsecured connections, and capture sensitive information.
- Phishing: Attackers trick individuals into revealing their personal information, passwords, or financial details through deceptive emails or websites.
- Malware: Malicious software, such as keyloggers or spyware, is used to capture data from compromised systems without the user's knowledge.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Attackers exploit security vulnerabilities in software or systems to gain unauthorized access and steal sensitive data.
3. Impact of Data Interception and Theft:
- Identity Theft: Stolen personal information can be used to impersonate individuals, commit fraud, or gain unauthorized access to accounts.
- Financial Loss: Data theft can lead to financial losses through unauthorized transactions, fraudulent activities, or the compromise of sensitive financial information.
- Privacy Breaches: Unauthorized access to personal or confidential data violates privacy rights and can result in personal or professional harm.
- Reputational Damage: Organizations that fail to protect data may suffer reputational damage, loss of trust, and a decline in customer confidence.
- Legal Consequences: Data interception and theft are illegal activities, and perpetrators can face legal consequences, including fines and imprisonment.
4. Protecting Against Data Interception and Theft:
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data to make it unreadable to unauthorized individuals who may intercept it.
- Strong Passwords: Use unique and strong passwords for accounts to prevent unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to accounts.
- Security Software: Install and regularly update antivirus, anti-malware, and firewall software to detect and prevent data breaches.
- Security Awareness: Educate yourself and others about common data security threats, such as phishing, and practice safe browsing habits.
The Concept of SQL Injection
SQL injection is a security vulnerability that occurs when malicious SQL code is inserted into a database query. In this study guide, we will explore the concept of SQL injection, its significance, and the measures to prevent it. Understanding SQL injection is crucial for maintaining data security and protecting against potential attacks.
1. Understanding SQL Injection:
- Definition: SQL injection is a type of security vulnerability where an attacker manipulates input data to execute unauthorized SQL commands.
- How it Works: Attackers exploit poorly validated user input fields to inject malicious SQL code into a query, enabling them to perform unauthorized actions on the database.
- Significance: SQL injection attacks can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, data manipulation, or even the complete loss of sensitive information.
2. Common Techniques Used in SQL Injection:
- Malicious Input: Attackers input malicious code, such as SQL statements or special characters, into user input fields.
- Union-based Attacks: Attackers use the UNION operator to combine additional malicious queries with the original query, retrieving unauthorized data.
- Boolean-based Attacks: Attackers exploit true or false conditions to extract information or manipulate the behavior of the query.
- Time-based Attacks: Attackers introduce delays in the SQL query to infer information based on the response time.
- Error-based Attacks: Attackers intentionally trigger errors to reveal sensitive information about the database structure.
3. Impact of SQL Injection:
- Unauthorized Access: SQL injection can allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to databases, bypassing authentication mechanisms.
- Data Manipulation: Attackers can modify or delete data in the database, potentially causing data integrity issues.
- Data Breaches: Sensitive information stored in databases, such as personal or financial data, can be compromised and used for malicious purposes.
- Reputation Damage: Organizations that fall victim to SQL injection attacks may experience reputational damage and loss of customer trust.
- Legal Consequences: SQL injection attacks are illegal, and perpetrators can face legal consequences, including fines and imprisonment.
4. Preventing SQL Injection:
- Parameterized Queries: Use parameterized queries or prepared statements to separate SQL code from user input, preventing direct code injection.
- Input Validation: Validate and sanitize user input to ensure it meets expected criteria and does not contain malicious code.
- Least Privilege: Assign minimal necessary privileges to database accounts, reducing the potential impact of an attack.
- Regular Updates and Patches: Keep database systems and associated software up to date with the latest security patches.
- Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses.
Here's an example of SQL injection:
Suppose we have a website that accepts user input for a login form with the intention of retrieving the corresponding user data from the database. The SQL query used to retrieve the data might look like this:
```
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '<input_username>' AND password = '<input_password>';
```
Now, imagine a malicious user enters the following into the username field:
```
' OR '1'='1'; --
```
The resulting SQL query after the injection would look like this:
```
SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '' OR '1'='1'; --' AND password = '<input_password>';
```
In this case, the injected code `' OR '1'='1'; --` manipulates the query to always evaluate the condition `'1'='1'`, which is always true. This means that the query will return all user records from the database, effectively bypassing the intended login mechanism.
The consequences of successful SQL injection can vary depending on the system and the attacker's intentions. It could lead to unauthorized access, exposure of sensitive data, or even the ability to execute arbitrary SQL commands on the database.
It is crucial to implement proper input validation, parameterized queries, and other security measures to prevent SQL injection attacks and protect the integrity and security of the database.