The Internet as a worldwide collection of computer networks
Subtopic 1: DNS (Domain Name Service)
DNS is a system that translates domain names (such as www.google.com) into IP addresses (such as 74.125.224.72).
DNS is made up of multiple domain name servers (DNS servers) that work together to provide this translation.
The significance of DNS is that it allows users to access websites and other resources on the Internet using domain names instead of IP addresses.
Practice question: What is DNS and how does it work? Why is it important for accessing websites on the Internet?
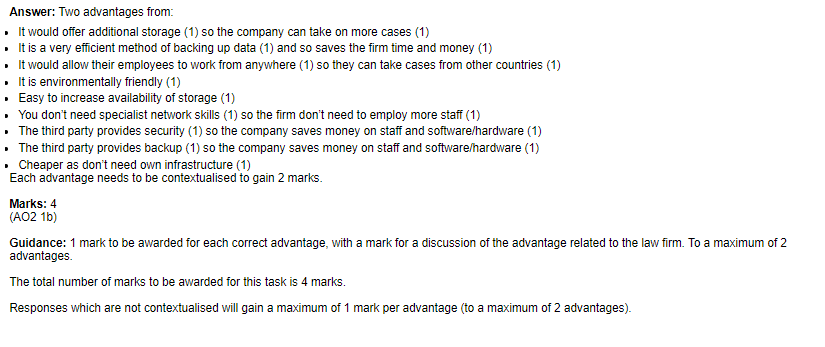
Subtopic 2: Concept of servers providing services (e.g. Web server - web pages, File server - file storage/retrieval)
Servers are computers that provide resources or services to other computers or devices on a network.
Web servers provide web pages and other resources to clients over the Internet, while file servers provide file storage and retrieval services.
The significance of servers providing services is that it allows users to access resources and services over a network.
Practice question: What is a server and what are some common types of services provided by servers?
Subtopic 3: Concept of clients requesting/using services from a server
Clients are computers or devices that request and use services provided by servers.
Clients can access services provided by servers over a network, such as the Internet.
The significance of clients using services from servers is that it allows users to access resources and services that are not available locally on their own device.
Practice question: What is a client and how does it use services provided by servers?
Subtopic 4: The Cloud: remote service provision (e.g. storage, software, processing)
The Cloud is a network of remote servers that provide various services, such as storage, software, and processing power, over the Internet.
Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an Internet connection and can be scaled up or down as needed.
The significance of the Cloud is that it allows users to access and use resources and services without needing to have them physically stored on their own device.
Practice question: What is the Cloud and what are some of the advantages of using cloud services?
Subtopic 5: A DNS’s role in the conversion of a URL to an IP address
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address used to access resources on the Internet, such as a website.
When a user enters a URL into a web browser, the browser uses DNS to convert the URL into an IP address that can be used to locate the resource on the Internet.
The significance of DNS in converting a URL to an IP address is that it allows users to access resources on the Internet using human-readable domain names instead of numerical IP addresses.
Practice question: How does DNS convert a URL to an IP address? Why is this conversion important for accessing resources on the Internet?
Overall, understanding the Internet as a worldwide collection of computer networks and the various components that make it up is essential for navigating the digital world and accessing information and resources. By understanding DNS, servers and clients, the Cloud, and the role of DNS in converting URLs to IP addresses, students can develop a deeper appreciation for the technology that connects the world and helps us communicate and collaborate on a global scale.
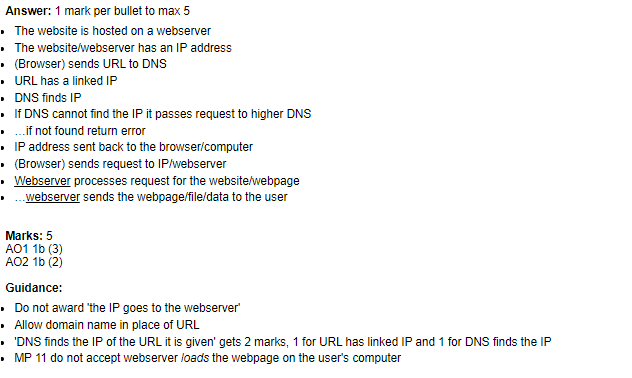
Here are the steps involved in typing a URL to viewing a website, and the role of DNS in the process:
- The user types the URL (Uniform Resource Locator) of the website they want to visit into their web browser, such as www.example.com.
- The web browser sends a request for the website to the user's Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- The ISP routes the request to a DNS server, which translates the domain name in the URL (e.g. www.example.com) into an IP address that identifies the specific server hosting the website.
- The DNS server returns the IP address to the user's web browser.
- The web browser uses the IP address to send a request for the website to the server hosting the website.
- The server hosting the website sends the website's files and resources back to the user's web browser.
- The user's web browser assembles the website's files and resources and displays the website to the user.
The role of DNS in this process is to translate the domain name in the URL (e.g. www.example.com) into an IP address that identifies the specific server hosting the website. Without DNS, users would have to remember and enter numerical IP addresses instead of human-readable domain names to access websites on the Internet. DNS allows users to access websites using easy-to-remember domain names, and it also makes it easier for website owners to change the location of their website without requiring users to update their bookmarks or remember a new IP address. Overall, DNS plays a crucial role in enabling the Internet to function as a worldwide collection of computer networks by allowing users to easily access and communicate with each other and with resources on the Internet.
Past Paper Questions