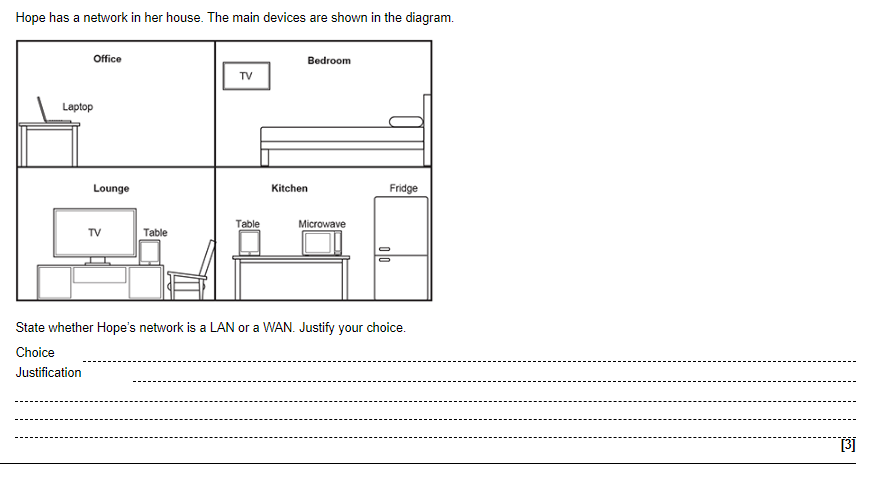
Types of network:
LAN (Local Area Network)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network that connects devices within a relatively small area, such as a home, school, or office building. LANs typically use Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi to connect devices, and may be controlled by a central server or switch. Some common examples of LANs include home networks, school networks, and office networks.
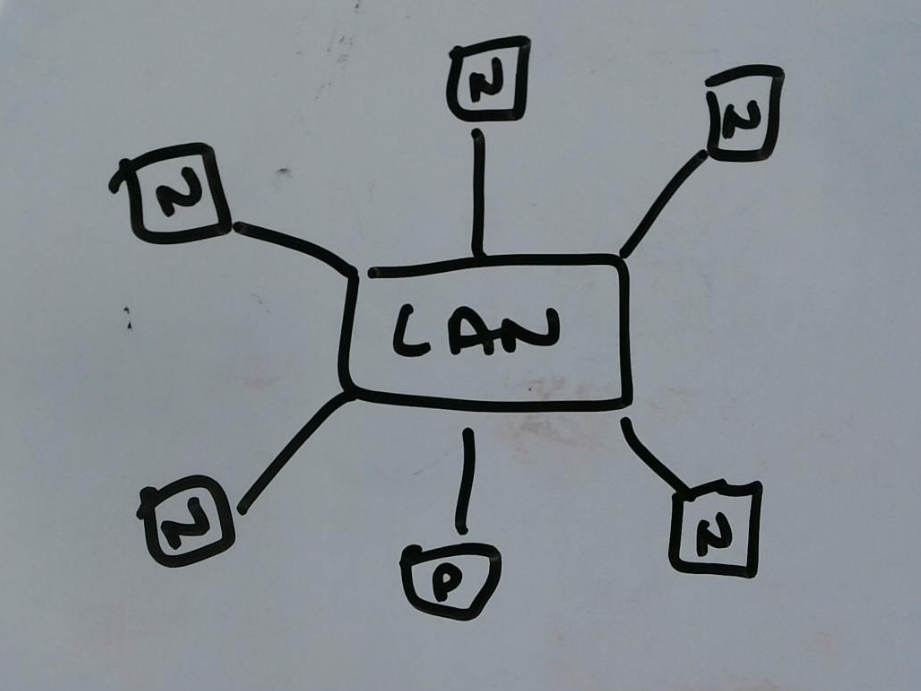
WAN (Wide Area Network)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that connects devices over a larger geographic area, such as multiple cities or countries. WANs typically use telecommunication links, such as fiber-optic cables or satellite connections, to connect devices. WANs are often used by businesses, governments, and organizations to connect remote locations and provide access to the Internet.
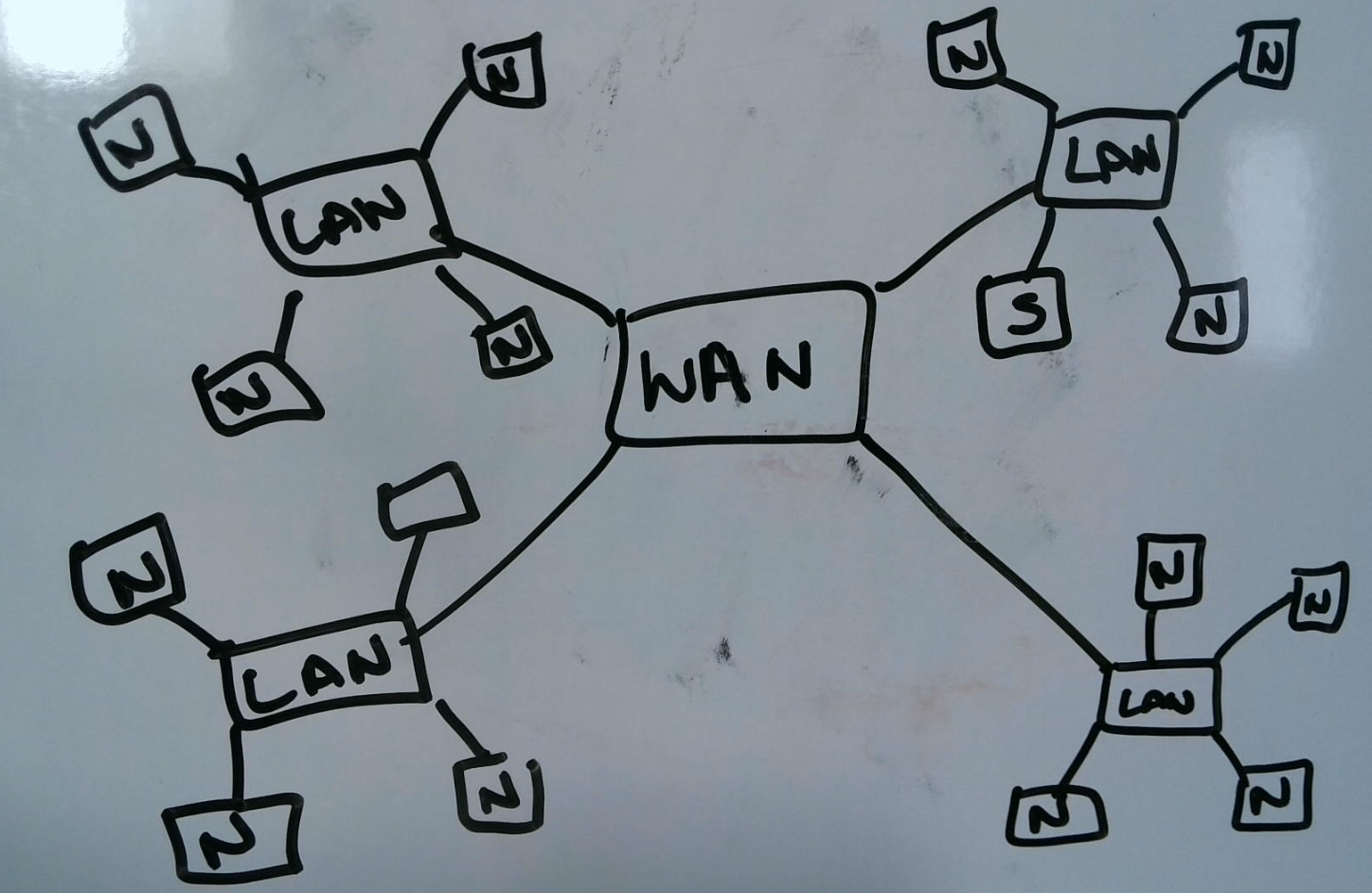
Characteristics of LANs and WANs
LANs and WANs have several characteristics that distinguish them from each other:
- Size: LANs are typically smaller and cover a smaller geographic area than WANs
- Speed: LANs are typically faster than WANs, since they have fewer devices and shorter distances between them
- Ownership: LANs are often owned and controlled by a single organization, while WANs may be owned and controlled by multiple organizations
- Cost: LANs are often less expensive to set up and maintain than WANs, which may require more complex infrastructure and equipment
- Security: LANs are generally more secure than WANs, since they are under the control of a single organization and are not exposed to the public Internet
Common Examples of LANs and WANs
Some common examples of LANs include:
- Home networks
- School networks
- Office networks
Some common examples of WANs include:
- The Internet
- Corporate networks that span multiple locations
- Government networks that connect multiple agencies and departments
Practice Questions
- What is a LAN?
- What is a WAN?
- What are some characteristics that distinguish LANs from WANs?
- What are some common examples of LANs and WANs?
- Why are LANs generally more secure than WANs?
Practice Answers
- A Local Area Network that connects devices within a relatively small area.
- A Wide Area Network that connects devices over a larger geographic area.
- LANs are typically smaller and cover a smaller geographic area than WANs; LANs are often owned and controlled by a single organization, while WANs may be owned and controlled by multiple organizations; LANs are generally less expensive to set up and maintain than WANs; LANs are generally more secure than WANs.
- Common examples of LANs include home networks, school networks, and office networks. Common examples of WANs include the internet, the telephone network, and the global positioning system (GPS).
- LANs are generally more secure than WANs because they are smaller and more easily controlled, and because they are not accessible to the wider public. Additionally, LANs can use security measures such as firewalls and access control lists to protect against unauthorized access.
Past Exam Questions